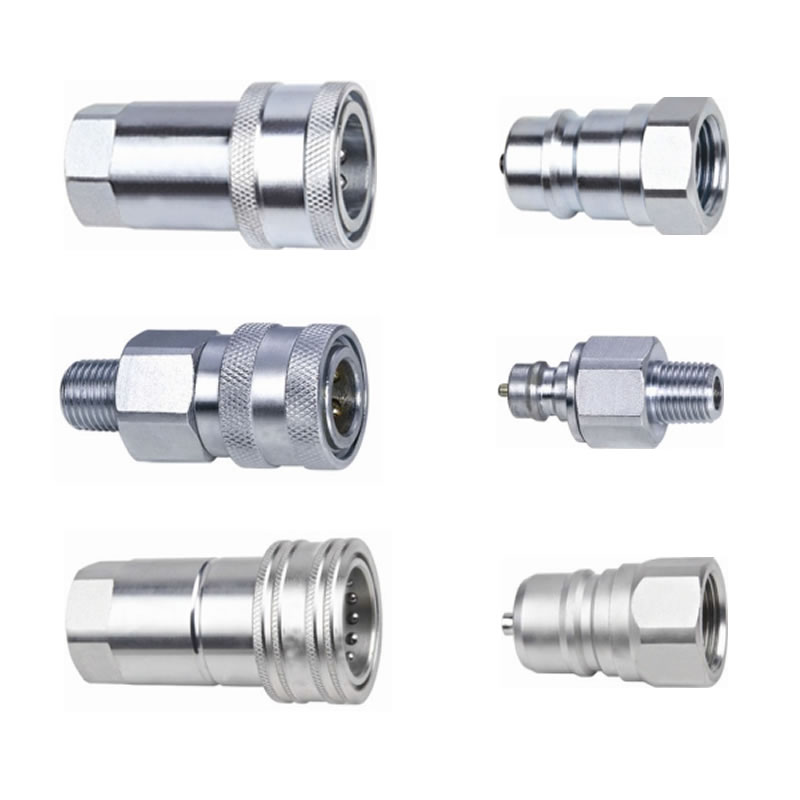
Hydraulic and Pneumatic Quick Disconnect Couplings
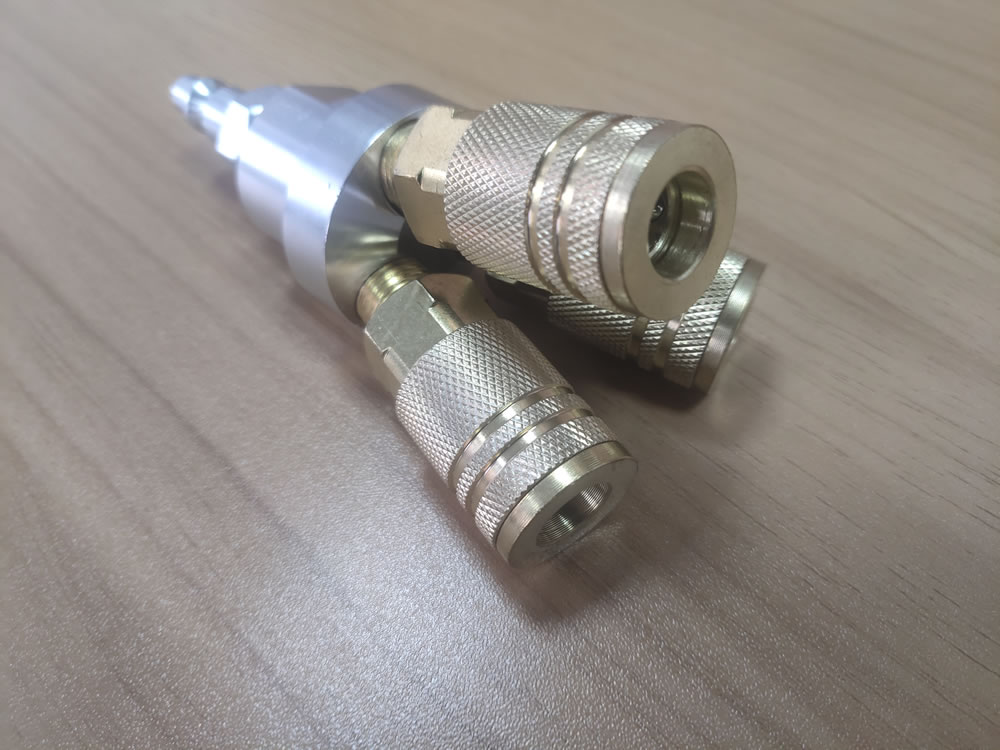

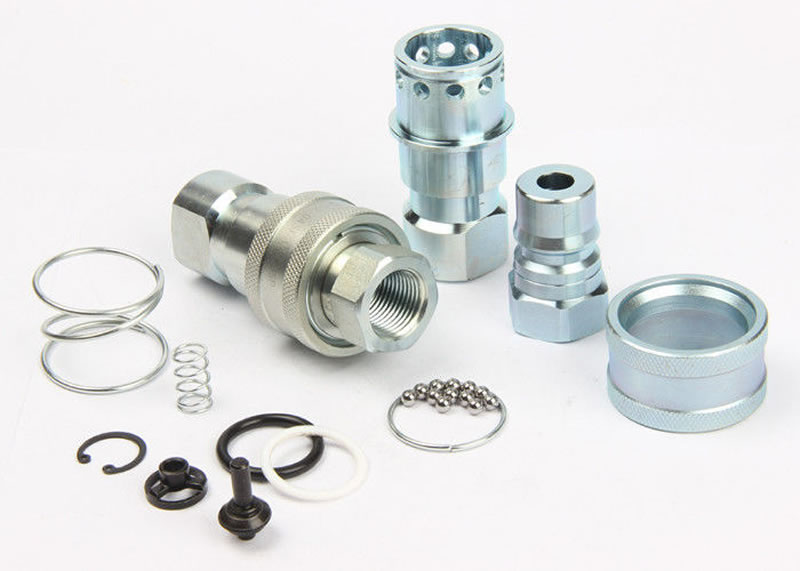
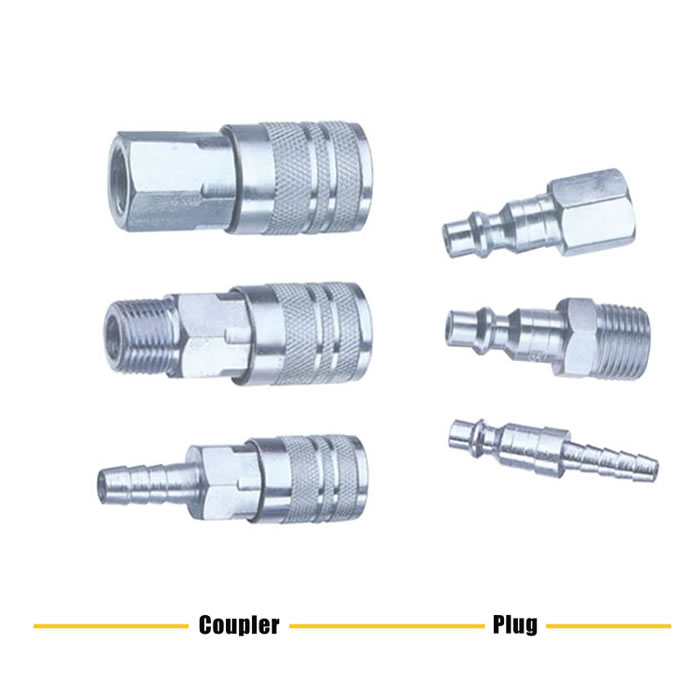
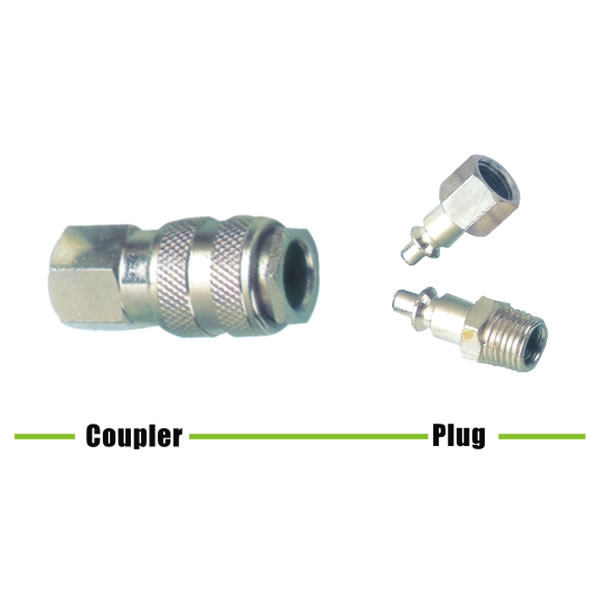
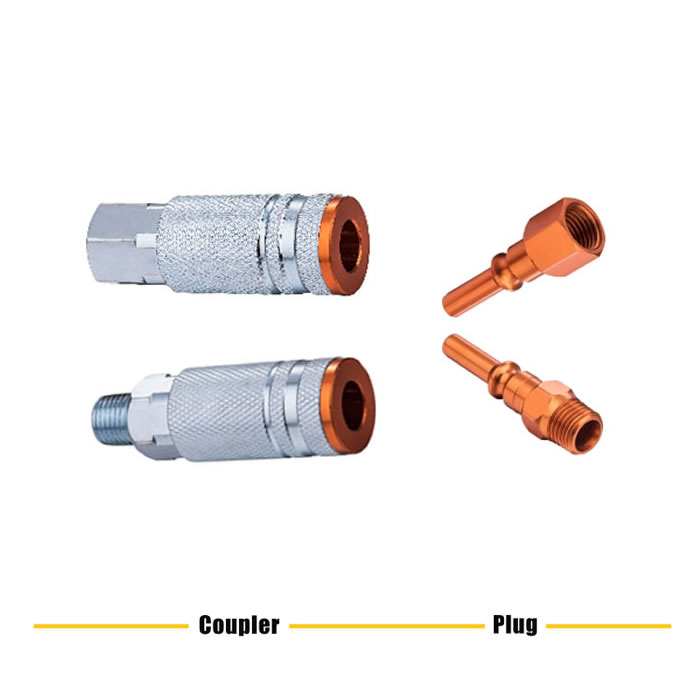
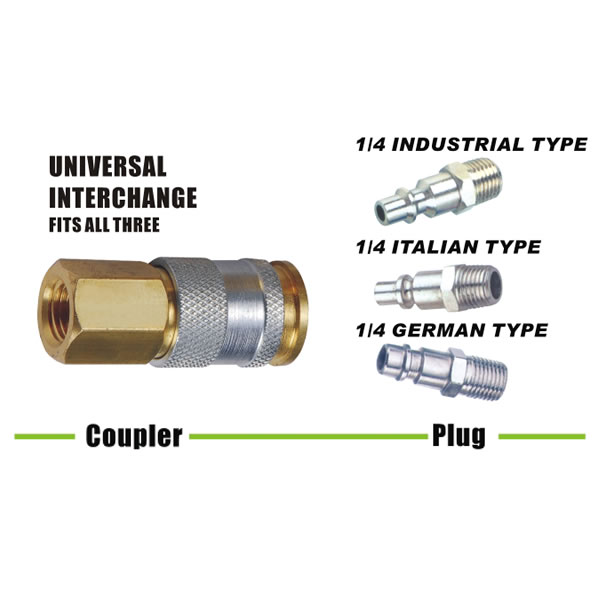
Quick disconnect couplings are widely used. The couplings are designed especially to provide a connection where ease of use, without tools is essential and in situations where the connection and disconnection of lines need to made quickly, smoothly and repetitively. One half is usually attached to a flexible line. Quick disconnect couplings are made up of two mating parts. Coupling are a female half and a male half. The female half is referred to as either the ‘Socket’ or the ‘Coupler’ or ‘Coupler Body’, and the male half is called either the ‘Plug’ or the ‘Nipple’ or ‘Nipple Body’.
Quick disconnect couplings, also known as quick couplers or quick disconnect fittings, are often used in situations where a hose has to be connected and disconnected quickly and efficiently. Because of environmental and cleanup concerns, pneumatic/hydraulic hose leaks are to be avoided at all costs. Quick disconnects minimize leakage, pressure drops and provide the ideal solution to difficult assemblies.
Why use a quick disconnect coupling over a conventional threaded connection?
Traditional threaded fitting:
No shut-off system: leakage after disconnection
> Cannot rotate while connected - line twisting decreases life of hose
> Additional assembly time
> Difficult handling, waste of time to disassemble (maintenance)
> Frequent disconnection effects seating performance, increases likelihood of leaking
Quick disconnect coupling:
Shut-off system: sealing achieved upon disconnection
> Can rotate while connected, taking stress out of hose and extending life
> Ease of assembly in tight spaces
> Easy and fast to use (without tool), time saving and economical
> Increased mobility and access for maintenance
What is a quick-disconnect coupling used for
Both pneumatic and hydraulic applications can benefit from quick disconnect couplings. (Sometimes you will see pneumatic quick disconnects referred to as air couplers.) Depending upon the material and configuration, quick disconnects can be used in the transference of air, hydraulic fluid, oil, water, chemicals or gas.
The markets where hoses need to be disconnected quickly and efficiently are varied, and these couplings can be used in almost any situation where fluid is being transferred by hose. They are used in agricultural applications, such as tractors and Harvesters, as well as in construction equipment (i.e., compact wheel loaders or crawler cranes) and industrial stationary equipment&tools (i.e., test benches or rolling mills).
Different types of quick disconnect couplings
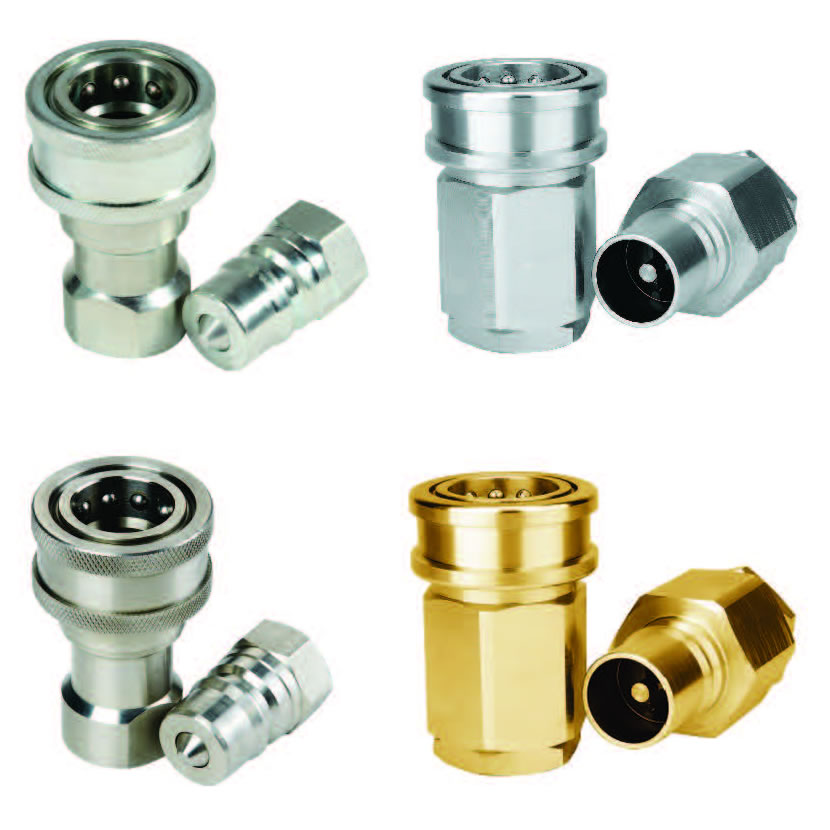
According to the specific fluids involved by the application, quick disconnect couplings are made out of different materials:
Pneumatic quick disconnect couplings in brass steel and stainless steel
Power tools can either be pneumatically or hydraulically powered, and since they need to be changed out frequently, quick disconnects are the easiest, cleanest, safest and most cost-effective way to achieve the desired result.
Quick disconnects are made from various different materials based upon the requirements of the job. In air applications, they can be plastic, brass, steel and PVC.
The connection options are push-to-connect and thread-to-connect. Hydraulic quick disconnects are available in steel, stainless steel and brass, and can either be push-to-connect or thread-to-connect.
It is important to take into account the pressure, temperature and size requirements for your quick disconnects. Get top-of-the line equipment to ensure that you can quickly and efficiently remove attachments.
What are carbon Steel quick couplings
The most commonly used carbon steel quick disconnect couplings are extremely tough, and resistant to pressures and tear & wear involved in daily use. NBR is the most popular compound for seals, other compounds can be used depending on the chemical compatibility needed by different fluids. FKM (Viton) in particular allows the quick couplings to have a broad working temperature range and makes them suitable for a wider range of applications. Faster catalog offers the largest selection of Carbon Steel quick couplings, able to answer various market requests and meet specific requirements by different manufacturers and end users.
What are brass quick couplings
Brass quick couplings are resistant to corrosion, durable and strong. This material makes the coupling highly robust and together with FKM (Viton) seals, it makes the couplings able to endure high temperatures. Faster products portfolio includes brass quick disconnects couplings suitable for industrial applications such as refrigeration systems, air conditioning and other applications with refrigerants, mold and die Industry, snubbing units for wells control and others.
What are stainless steel couplings quick release
Stainless Steel quick coupling is necessary when high resistance to corrosion is needed and it offers excellent resilience, for this reason it is often used to make quick couplers for applications characterized by corrosive fluids or harsh environment. Also, the stainless steel quick couplings are equipped with FKM (Viton) seals, thus offering a wider working temperature range, which makes them more versatile and suitable for tougher applications. Even when exposed to potentially corrosive fluids, stainless steel couplings are a guarantee of durability and resistance.
Fitting Ends And Quick Disconnect Coupling Types
The three most common fitting ends and connector types for hydraulic fittings are the O-ring, the mated angle, and the tapered thread connectors. Although these are the most popular choices, several other types are used in different and specialised applications.
Since hydraulic fittings vary in how they seal connections, it is important to consider seeking professional or technical advice to avoid leaks or other dangerous scenarios.
The primary fittings and connector types are:

O-Ring Face Seal (ORFS) – hydraulic fittings equipped with this kind of sealing method provide a secure and reliable elastomeric seal preferred for applications with any risk of leaking fluids. They can eliminate leaks in hydraulic systems that operate at pressures that can reach up to 6,000 psi. ORFS fittings can be split into the following types:
Straight ORFS Fitting – a straight screw connection with a male ORFS connection point to male PRT, G, or metric threads.
Elbow ORFS Fitting is an elbow screw connection with an ORFS female connection and an ORFS male connection at an angle.
Tee ORFS Fitting – this is a T-shaped screw connection with three connection ports. One is a female ORFS connection port, with two other male ORFS connection ports.
Cross ORFS Fitting – this is equipped with four male ORFS connection ports and is useful for distribution or combining.
DIN Or BSP – these stand for ‘Deutsches Institut für Normung’ and ‘British Standard Pipe’ and are a type of hydraulic fitting commonly used across Europe.
DIN hydraulic fittings are interchangeable with different brands of fittings. They are used in industrial, construction, and oil applications and industries.
BSP hydraulic fittings have screw threads that conform to BSP standards. These fittings are used primarily for interconnecting pipes and sealing, which is achieved by interlocking the external (male) with the internal (female) thread. These fittings are commonly found in plumbing industries and are widely accepted worldwide except for North America due to the American National Pipe Tapered Thread (NPT) standard.
Mated Angle – hydraulic fittings with an angle seat equipped with either straight or parallel threads for sealing. When the male and female counterparts are threaded together, the threads don’t actually form the seal. Instead, the fitting mechanically creates a seal by bringing the mating angle seats together, making the seal.
Tapered Threads – this type of hydraulic fitting has a male and female thread. Male fittings have their threads on the outside, while female fittings have theirs on the inside. The tapered thread deforms when the male and female fittings are threaded together. This consequently applies pressure on the couplings, which create the seal. Unfortunately, these fittings are prone to shredding and contaminate sensitive areas, which often causes them to be prohibited for use in hydraulic and pneumatic systems. In addition, the lubricity of these fittings has also been known to cause over-torquing.
| Port Connection | Hose Connection |
| BSPP (JISPF) | 60 degree NPSM Swivel |
| BSPT (JIS-PT) | 30 degree Flare (Metric) |
| DIN Metric | O-Ring Face Seal (ORFS) |
| ISO 6149 | 24 Degree Flareless (DIN) |
| JIS-B2351 | 30 Degree Flare (BSPP) |
| Metric Taper | 45 Degree Flare |
| NPT-NPTF | 37 Degree Flare |
| SAE Straight Thread | 24 Degree Flareless (SAE) |
You May Like
- ISO 7241 B Close Type Hydraulic Quick Connect Hose Coupling KZBLongwei Auto Parts2022-09-02T09:39:12+08:00


























Leave A Comment