What is NPT Thread (National Pipe Tapered threads)?
Faq,Tech Archives
June 15, 2016
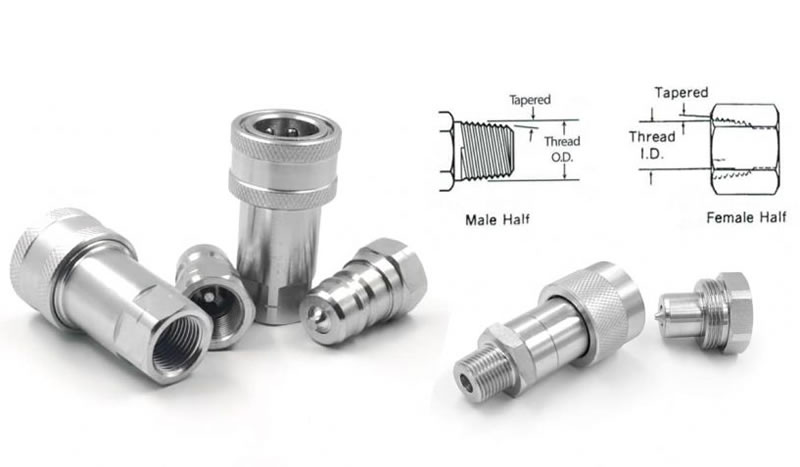
The NPT Thread stands for American National Standard Pipe Thread standards, often called national pipe thread standards for short, are U.S. national technical standards for screw threads used on threaded pipes and pipe fittings. also known as ANSI/ASME B1.20.1 pipe threads. It for measuring tapered threads on threaded pipes and fittings.
They include both tapered and straight thread series for various purposes, including rigidity, pressure-tight sealing, or both. Sometimes referred to as MPT (male pipe threads), NPT threads are not interchangeable with NPS (National Pipe Straight) threads. Unlike straight threads found on a bolt, a taper thread will pull tight, making a closer seal. A sealant compound or PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) tape must be used to ensure a leak-free seal. The types are named with a symbol and a full name. Examples of the symbols include NPT, NPS, NPTF, NPSC.
Outside North America, some US pipe threads are found, as well as many British Standard Pipe threads and ISO 7-1, 7-2, 228-1, and 228-2 threads.
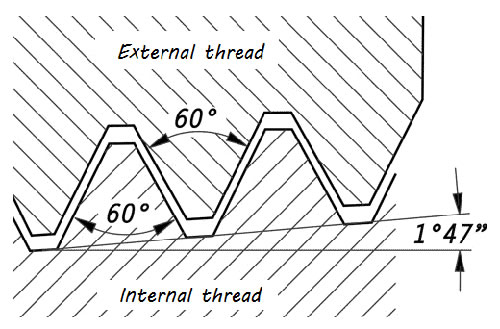
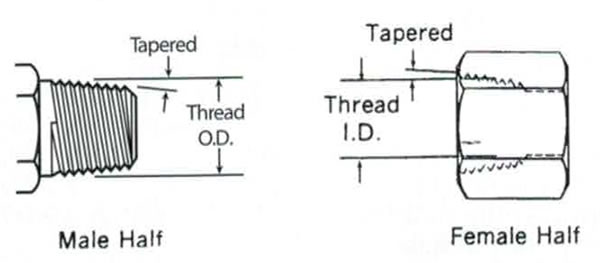
Characteristics of NPT:
angle between taper and center axis of pipe is 1° 47’ 24” (1.7800°)
truncation of roots and crests are flat
60° thread angle
pitch is measured in threads per inch (TPI)
Sizing
The NPT threads sizing chart includes data for external and internal pipe threads. The taper rate for all NPT threads is 1/16—3/4 in. per foot (62.5 mm per m)—which is measured by the change of diameter over distance. The outside diameter (OD) of a pipe or fitting must also be measured; both the TPI and OD are required for accurate identification of thread size because more than one size can have the same TPI.
Commonly used sizes include: 1/8, ¼, 3/8, ½, ¾, 1, 1 ¼, 1 ½, and 2 in. These can be found on pipes and fittings used by most U.S. suppliers. Sizes less than 1/8 in. are sometimes used for compressed air, while sizes more than 2 in. are less common, mainly because other joining methods are more often employed with these larger sizes.
Leakage issues associated with NPT
NPT threads were initially designed for water pipe plumbing (60 psi), not for hydraulic systems. However, they have been used in hydraulic systems for many years. Pipe threads in general are not recommended for high-pressure applications as they tend to leak more than any other style of connection. As previously mentioned, NPT requires some kind of sealant placed on the threads before assembly.
NPT threads are more likely to leak than their Dryseal counterparts; however, either thread type will leak if undertightened. A general tightening standard has yet to be established, but keep in mind that tightening requirements change with each re-use and/or type of sealant used. Also note that overtightening can crack the female port.
The various types are each named with a symbol and a full name
| Abbreviation | Shorthand expansion | Full name | Comment |
| NPT | National pipe taper | American National Standard Taper Pipe Thread | Tapered for sealing, often without any thread sealant; for connections in nearly every type of service |
| NPS | National pipe straight | American National Standard Straight Pipe Thread | For rigidity; sealable only with sealant; sometimes male straight enclosed by female tapered for low-pressure sealing |
| NPSC | National pipe straight–coupling | American National Standard Straight Pipe Thread for Couplings | For general couplings |
| NPSF | National pipe straight–fuel | Dryseal USA (American) Standard Fuel Internal Straight Pipe Thread | Internal only, straight |
| NPSH | National pipe straight–hose | American National Standard Straight Pipe Thread for Hose Couplings | For hose couplings |
| NPSI | National pipe straight–intermediate | Dryseal USA (American) Standard Intermediate Internal Straight Pipe Thread | Similar to NPSF but slightly larger; internal only, straight |
| NPSL | National pipe straight–locknut | American National Standard Straight Pipe Thread for Loose-fitting Mechanical Joints with Locknuts | For use with locknuts |
| NPSM | National pipe straight–mechanical | American National Standard Straight Pipe Thread for Free-fitting Mechanical Joints | For various rigid mechanical uses |
| NPTF | National pipe taper–fuel | Dryseal USA (American) Standard Taper Pipe Thread | For dryseal connections in nearly every type of service, especially fuel connections |
| NPTR | National pipe taper–railing | American National Standard Taper Pipe Thread for Railing Joints | For railings |
| PTF-SAE SHORT | Pipe taper, fuel, SAE, short | Dryseal SAE Short Taper Pipe Thread | Named after SAE International; similar to NPTF but one turn shorter |
Measuring for a leak-free seal
In the imperial system, TPI is measured by how many crests (threads) there are per inch; the metric system measures the distance between two crests.
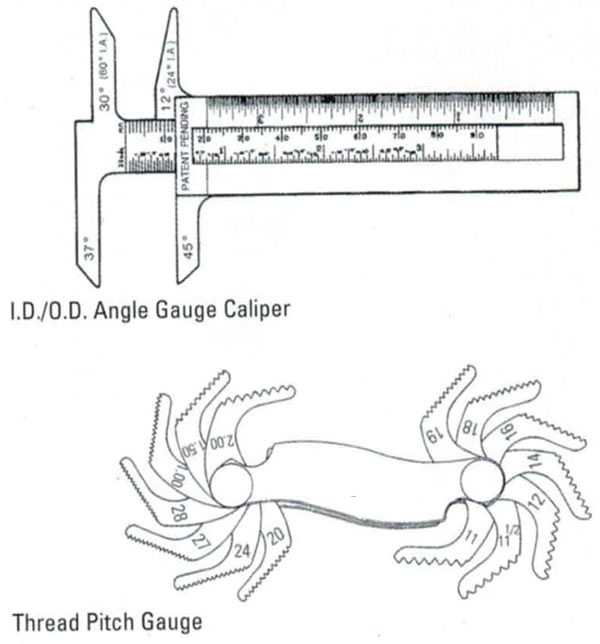
Using the trial-by-error method, try different thread gauges until you determine the tightest fit; engage as many threads as possible—the more threads engaged, the more accurate the reading. Hold the fitting and thread gauge up to the light, looking for gaps between the gauge and thread. This is easier to see on a male connection than a female one.
Next, measure the thread diameter with an ID/OD caliper. Male thread diameter is measured on the OD; female thread diameter is measured on the ID. The Hose Safety Institute Handbook recommends holding the caliper at a slight angle for a more accurate male reading, and holding it perpendicular to the thread for a more accurate female reading.
If the pipe or fitting connection seals on a flared surface or inverted angle seat, determine that angle of seal with a seat angle gauge on the male connection. Place the gauge on the sealing surface; if the centerlines of connection and gauge are parallel, the correct angle has been determined. For a female connection, insert the gauge into the connection and place it on the sealing surface. As with the male connection, if the centerlines are parallel, the correct angle has been determined.
NPT Threads Dimensions
| NPT THREAD SIZE & PITCH |
DASH SIZE |
MALE THREAD MINOR OD |
FEMALE THREAD ID |
||
| inch – TPI | mm | inch | mm | inch | |
| 1/8 – 27 | -02 | 9,9 | 0.39 | 8,4 | 0.33 |
| 1/4 – 18 | -04 | 13,2 | 0.52 | 11,2 | 0.44 |
| 3/8 – 18 | -06 | 16,6 | 0.65 | 14,7 | 0.58 |
| 1/2 – 14 | -08 | 20,6 | 0.81 | 17,8 | 0.70 |
| 3/4 – 14 | -12 | 26,0 | 1.02 | 23,4 | 0.92 |
| 1 – 11.1/2 | -16 | 32,5 | 1.28 | 29,5 | 1.16 |
| 1.1/4 – 11.1/2 | -20 | 41,2 | 1.62 | 38,1 | 1.50 |
| 1.1/2 – 11.1/2 | -24 | 47,3 | 1.86 | 43,9 | 1.73 |
| 2 – 11.1/2 | -32 | 59,3 | 2.33 | 56,4 | 2.22 |
| 2.1/2 – 8 | -40 | 71,5 | 2.82 | 69,1 | 2.72 |
| 3 – 8 | -48 | 87,3 | 3.44 | 84,8 | 3.34 |
NPSM Threads Dimensions
| NPSM THREAD SIZE |
DASH SIZE |
FEMALE THREAD ID |
|
| inch – TPI | mm | inch | |
| 1/8 – 27 | -02 | 8,6 | 0.34 |
| 1/4 – 18 | -04 | 11,9 | 0.47 |
| 3/8 – 18 | -06 | 15,0 | 0.59 |
| 1/2 – 14 | -08 | 19,1 | 0.75 |
| 3/4 – 14 | -12 | 24,6 | 0.97 |
| 1 – 11.1/2 | -16 | 30,5 | 1.20 |
| 1.1/4 – 11.1/2 | -20 | 39,4 | 1.55 |
| 1.1/2 – 11.1/2 | -24 | 45,5 | 1.79 |
| 2 – 11.1/2 | -32 | 57,4 | 2.26 |
| 2.1/2 – 8 | -40 | 68,8 | 2.71 |
| 3 – 8 | -48 | 84,6 | 3.33 |









