What are NPT, BSP, JIS, SAE, Metric
Faq,Tech Archives
July 18, 2016
It's important to identify the specific thread type of the Quick Coupler you need in order for your equipment to function at its best. Pneumatic components such as air cylinders, valves, and air preparation units come equipped with specific port threads.
For example, the pneumatic components we offer in our web store are available with either NPT, PT or G port threads. Choosing the correct thread type will ensure optimum compatibility with your equipment.
At a glance, threads may look similar. But take a closer look and you'll notice the very subtle differences that would make them incompatible with one another. For example, G threads are not compatible NPT threads because of their differing angles, shapes, and thread pitches (threads per inch).
We have compiled a simple step-by-step guide to help you identify your thread type. In addition, we'll cover some of the most common port thread types including NPT/NPTF, BSPP (also known as G), BSPT, PT, Metric (M) and SAE. You'll need a couple tools on hand to make the process easier, but a straight steel ruler may work as well.
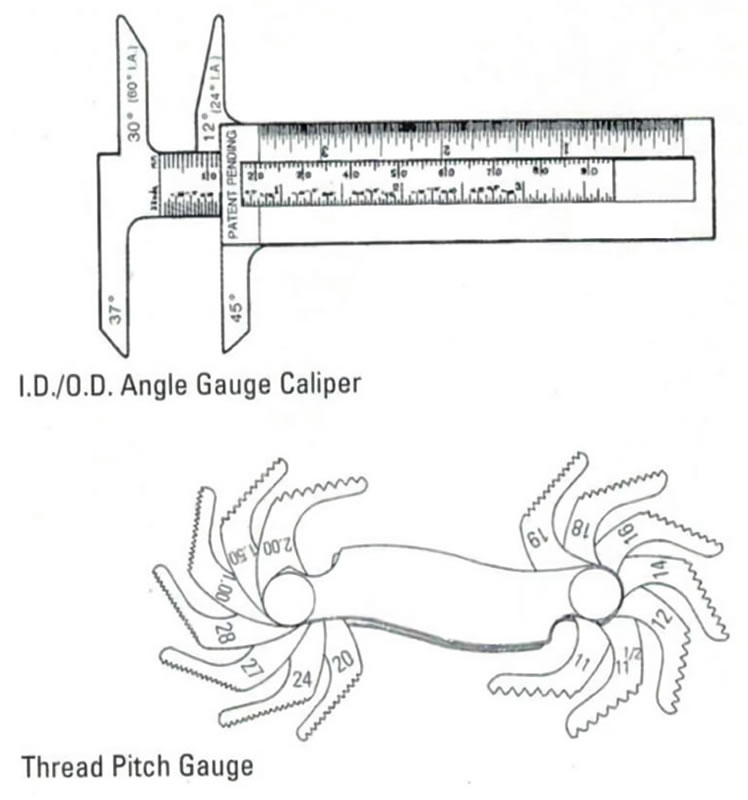
Caliper –
A caliper is a useful tool that measures the outside diameter of a male thread and inside diameter of a female thread. Using a caliper will give you the most accurate and precise measurements, but a straight steel ruler is a good alternative.
Pitch Gauge –
A pitch gauge measures the threads per inch. For metric threads, this tool measures the distance between the threads.
How to Identify Different Types of Threads
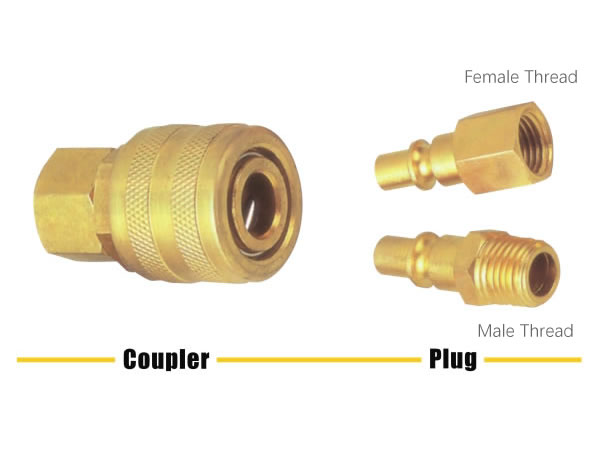
Step 1 – Male Threads vs Female Threads
First, you'll need to identify whether the thread type is male or female. Take a look at where the threads are located. If they're on the outside of the thread, it's a male thread. If they‘re on the inside of the thread, it's a female thread.
The gender of the thread doesn't necessarily have an impact on the functionality of the thread. It simply serves as a way to distinguish between the two connections.
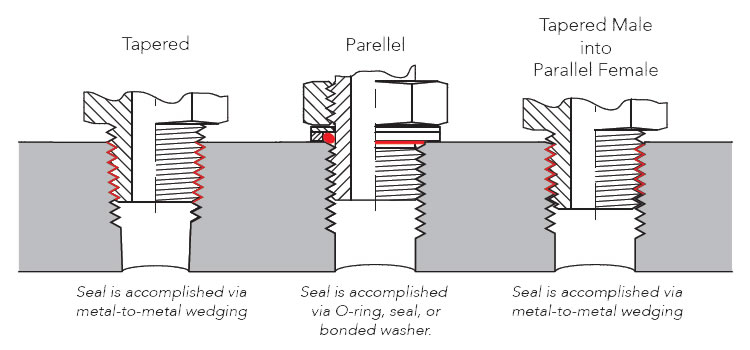
Step 2 – Tapered Threads v. Parallel Threads
Next, determine if the thread is tapered or parallel. Tapered threads become narrower as they extend outward while parallel threads remain the same diameter. Sometimes this characteristic can be determined through visual inspection, but if not a caliper can come in handy. Use the caliper to measure the first, fourth, and final full thread. If the measurements are all the same, then it's parallel. If the measurements decrease in size, then it's tapered.
NPT/NPTF, BSPT, and Metric Tapered are examples of tapered threads. These threads create a seal through metal-to-metal wedging or slight deformation of the threads. Parallel threads will often require an o-ring or thread tape to ensure a tight seal.
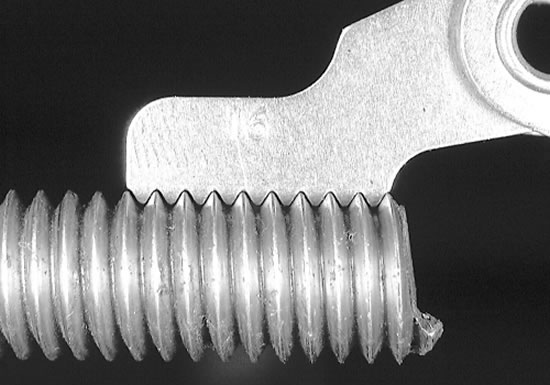
Step 3 – Pitch Size
The next step in identifying your thread type is to determine the pitch size. A thread's pitch size is the number of threads per inch or the distance between threads on metric thread types. While a ruler could be used to calculate the pitch size, a pitch gauge is highly recommended as pitch sizes can be very similar.
Test a couple different sizes with a pitch gauge to find the best match.
Step 4 – Thread Diameter
After you've figured out the pitch size, you'll need to determine the thread diameter. Using the caliper again, measure the outside diameter on a male thread and inside diameter on a female thread.
If you find that your measurements don't exactly line up with the measurements in the tables below, this is okay. There will inevitably be small variations due to different manufacturers.
Step 5 – Thread Type Standard
The final step in identifying your thread type is to identify the thread type standard. NPT, PT, and G are all examples of thread type standards. Gather the information from the previous steps and compare it with the measurements in the tables below.
Note: Due to variations in manufacturing the thread diameter may not match exactly with the measurements below.
NPT/NPTF Thread Type – National Pipe Tapered Fuel
This thread type is most commonly used in North America. You'll recognize it by its tapered outer and inner diameter which is self-sealing. When torqued the flanks of the threads compress against each other forming a leak-tight seal. However, it is still recommended to use PTFE tape or another sealant compound to guarantee a completely leak-tight seal.
A semi-compatible variant of NPT is NPTF (National Pipe Taper Fuel). It ensures an even more leak-free seal. But it is important to note that using these variants together diminishes their leak-free characteristics.
NPT threads should be burr-free and lubricated using lubricating paste or tape. Doing so limits corrosion on the threads which otherwise can make future disassembly nearly impossible.
| Dash Size(Nominal Size) | Thread Pitch | Male Thread O.D. mm | Male Thread O.D. inches | Female Thread I.D. mm | Female Thread I.D. inches |
| -02 (1/8) | 27 | 10.3 | 0.41 | 9.4 | 0.37 |
| -04 (1/4) | 18 | 13.7 | 0.54 | 12.4 | 0.49 |
| -06 (3/8) | 18 | 17.3 | 0.68 | 15.7 | 0.62 |
| -08 (1/2) | 14 | 21.3 | 0.84 | 19.3 | 0.76 |
| -10 (5/8) | 14 | 22.9 | 0.90 | 21.1 | 0.83 |
| -12 (3/4) | 14 | 26.9 | 1.06 | 24.9 | 0.98 |
| -16 (1) | 11½ | 33.3 | 1.31 | 31.5 | 1.24 |
| -20 (1 ¼) | 11½ | 42.2 | 1.66 | 40.1 | 1.58 |
| -24 (1 ½) | 11½ | 48.3 | 1.90 | 46.2 | 1.82 |
| -32 (2) | 11½ | 60.4 | 2.38 | 57.9 | 2.29 |
*O.D. = Outside Diameter I.D. = Inside Diameter
BSP Thread Type – British Standard Pipe
This is a standard thread type that has been adopted internationally for interconnecting and sealing pipe ends. You'll find it used all throughout Europe.
There are two types of BSP threads, BSPP and BSPT.
BSPP refers to parallel or straight threads.
BSPT refers to tapered threads.
Sometimes BSPP threads are referred to as G threads and BSPT threads as R threads. Are you confused yet?
Note: JIS tapered pipe thread (PT thread) is interchangeable with BSPT thread.
| Dash Size(Nominal Size) | Thread Pitch | Male Thread O.D. mm | Male Thread O.D. inches | Female Thread I.D. mm | Female Thread I.D. inches |
| -02 (1/8) | 28 | 9.7 | 0.38 | 8.9 | 0.35 |
| -04 (1/4) | 19 | 13.2 | 0.52 | 11.9 | 0.47 |
| -06 (3/8) | 19 | 16.5 | 0.65 | 15.2 | 0.60 |
| -08 (1/2) | 14 | 20.8 | 0.82 | 19.1 | 0.75 |
| -10 (5/8) | 14 | 22.4 | 0.88 | 20.3 | 0.80 |
| -12 (3/4) | 14 | 26.4 | 1.04 | 24.6 | 0.97 |
| -16 (1) | 11 | 33.0 | 1.30 | 31.0 | 1.22 |
| -20 (1 ¼) | 11 | 41.9 | 1.65 | 39.6 | 1.56 |
| -24 (1 ½) | 11 | 47.8 | 1.88 | 45.5 | 1.79 |
| -32 (2) | 11 | 59.7 | 2.35 | 57.4 | 2.26 |
*O.D. = Outside Diameter I.D. = Inside Diameter
JIS Tapered Pipe Thread Type – PT
PT thread type is identical and interchangeable with BSPT thread type. However, since the male PT thread does not have a 30-degree flare, it will not mate with the BSPP female swivel with conical seat. Also, we recommended using thread sealant with PT threads to ensure a leak-free seal.
| Dash Size(Nominal Size) | Thread Pitch | Male Thread O.D. mm | Male Thread O.D. inches | Female Thread I.D. mm | Female Thread I.D. inches |
| -02 (1/8) | 28 | 9.4 | 0.37 | 8.1 | 0.32 |
| -04 (1/4) | 19 | 13.7 | 0.53 | 12.4 | 0.49 |
| -06 (3/8) | 19 | 17.2 | 0.68 | 16 | 0.62 |
| -08 (1/2) | 14 | 21.5 | 0.84 | 19.8 | 0.77 |
| -10 (5/8) | 14 | 23.1 | 0.91 | 20.6 | 0.81 |
| -12 (3/4) | 14 | 26.9 | 1.06 | 25.4 | 1 |
| -16 (1) | 11 | 34 | 1.34 | 31.8 | 1.25 |
| -20 (1 ¼) | 11 | 42.6 | 1.68 | 40.4 | 1.59 |
| -24 (1 ½) | 11 | 48.5 | 1.9 | 46.2 | 1.81 |
| -32 (2) | 11 | 60.4 | 2.37 | 58.2 | 2.29 |
*O.D. = Outside Diameter I.D. = Inside Diameter
SAE Thread Type – Straight Thread O-Ring Boss
SAE - Society of Automotive Engineers - straight threads are able to seal because of the 90-durometer Buna-N “O” Ring. This is a highly reliable and reusable thread type. While some thread types require the threads of the male and female end to crush together to form a seal, the O-Ring on this thread type prevents that.
| Dash Size(Nominal Size) | Thread Pitch | Male Thread O.D. mm | Male Thread O.D. inches | Female Thread I.D. mm | Female Thread I.D. inches |
| -02 (1/8) | 24 | 3.9 | 0.31 | 6.9 | 0.27 |
| -03 (3/16) | 24 | 9.6 | 0.38 | 8.6 | 0.34 |
| -04(1/4) | 20 | 11.2 | 0.44 | 9.9 | 0.39 |
| -05(5/16) | 20 | 12.7 | 0.5 | 11.4 | 0.45 |
| -06(3/8) | 18 | 14.2 | 0.56 | 12.9 | 0.51 |
| -08(1/2) | 16 | 19 | 0.75 | 17 | 0.67 |
| -10(5/8) | 14 | 22.3 | 0.88 | 20.3 | 0.8 |
| -12(3/4) | 12 | 26.9 | 1.06 | 24.9 | 0.98 |
| -14(7/8) | 12 | 30 | 1.18 | 27.7 | 1.09 |
| -16(1) | 12 | 33.3 | 1.31 | 31 | 1.22 |
| -20(1 ¼) | 12 | 41.4 | 1.63 | 39.1 | 1.54 |
| -24(1 ½) | 12 | 47.7 | 1.88 | 45.5 | 1.79 |
| -32(2) | 12 | 63.5 | 2.5 | 61.2 | 2.41 |
*O.D. = Outside Diameter I.D. = Inside Diameter
Metric Tapered/Parallel Thread Type
Metric thread type is most common in Europe. It has a cylindrical inner and outer diameter precise in millimeters. The fine taper of metric tapered thread allows for the best possible force transmission.
In writing, you can identify metric threads by a capital “M” plus an indication of their nominal outside diameter (ex. M22 x 1.5). Lastly, when measuring pitch size make sure you‘re using a metric pitch gauge.
| SI Metric Port Size mm | Thread Pitch mm | Male Thread O.D. mm | Male Thread O.D. inches |
| M5 × 0,8 | .8 | 5 | 0.1968 |
| M8 × 1,0 | 1 | 8 | 0.3150 |
| M10 × 1,0 | 1 | 10 | 0.3937 |
| M12 × 1,5 | 1.5 | 12 | 0.4724 |
| M14 × 1,5 | 1.5 | 14 | 0.5512 |
| M16 × 1,5 | 1.5 | 16 | 0.6299 |
| M18 × 1,5 | 1.5 | 18 | 0.7087 |
| M22 × 1,5 | 1.5 | 22 | 0.8661 |
| M27 × 2,0 | 2 | 27 | 1.063 |
| M33 × 2,0 | 2 | 33 | 1.299 |
| M42 × 2,0 | 2 | 42 | 1.654 |
| M50 × 2,0 | 2 | 50 | 1.969 |
| M60 × 2,0 | 2 | 60 | 2.362 |
*O.D. = Outside Diameter
Alternative Thread Solutions
variety of cost-effective replacement pneumatic parts. need to know is the thread type. you have three options: NPT, PT, or G (BSPP).
Here's how we can get around all that if you're in a pinch.
1. Do you know where your equipment was manufactured? If your equipment is originally from China, 9 times out of 10 you‘ll need PT threads. If it was manufactured in North America, then you‘re safe to go with NPT threads. You may need to reference the user manual to find this information or contact the original equipment manufacturer.
2. Does your product require fittings? Let‘s say you have a pneumatic filter with NPT threads. It may be possible to simply replace these fittings to make them compatible with a PT threaded product.
3. For dire situations, use PFTE thread seal tape. As a last resort, you can use sealant tape to mate PT and NPT threads together. We recommend this as a last resort though.
You may be interested in our range of Longwei Air Fittings including adaptors, quick coupler connectors, tire gauges, air blow gun, air chuck and tire repair tools kit, etc. If you have any further questions about the type of thread fitting you require, please contact the Longwei team today!








