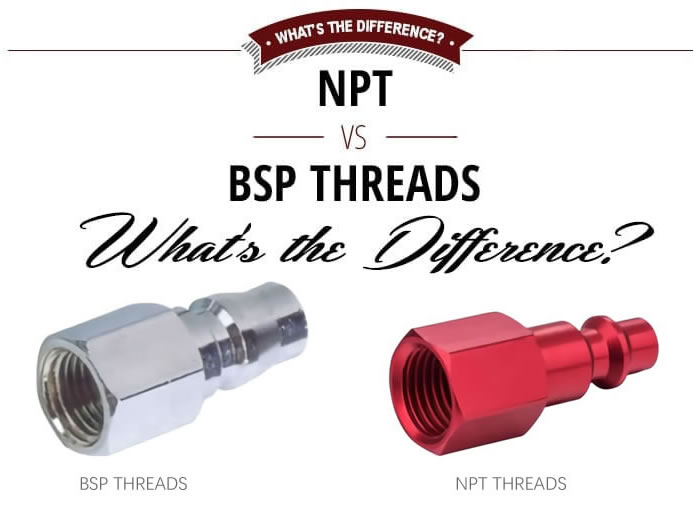
BSP vs NPT Thread What’s the Difference?
Tech Archives
July 18, 2016
The two most popular thread styles of the Quick Couplings in the world are British Standard Pipe (BSP) and National Pipe Taper (NPT). They are the international standard for joining fittings and pipes. However, the difference between these thread styles is something to note.
BSP thread form stands for British Standard Pipe and is common in Australia and the commonwealth countries. It is based on trade size rather than actual diameter which can lead to some confusion when measuring ports. There are two types of BSP threads;
- BSPP - Female & male thread are both (also known as G)
- BSPT - Female thread is parallel and the male thread is tapered (also know as R/Rp) (the female thread can also be tapered it is then Rc, these are fairly rare to find). Within BSPT it is also common to call the female thread BSPP (parallel) and the male BSPT (tapered) even though they are both technically a BSPT thread form (the female would be parallel and the male would be tapered).
Both threads have the same pitch, angle (55 degrees) and shape (rounded peaks and valleys).The below table gives the major and minor diameter for each BSP Trade Thread Size. The minor diameter may be ever so slightly smaller than what is in the table depending upon where it has been manufactured to in the thread gauge.
| Trade Size | Threads per inch | Pitch | Major Diameter | Minor Diameter | Gage Length | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inch | mm | Inch | mm | Inch | Mm | Inch | mm | ||
| 1/8 | 28 | 0.0357 | 0.907 | 0.383 | 9.728 | 0.3372 | 8.565 | 0.1563 | 3.97 |
| 1/4 | 19 | 0.0526 | 1.337 | 0.518 | 13.157 | 0.4506 | 11.445 | 0.2367 | 6.012 |
| 3/8 | 19 | 0.0526 | 1.337 | 0.656 | 16.662 | 0.5886 | 14.95 | 0.25 | 6.35 |
| 1/2 | 14 | 0.0714 | 1.814 | 0.825 | 20.955 | 0.7336 | 18.633 | 0.3214 | 8.164 |
| 3/4 | 14 | 0.0714 | 1.814 | 1.041 | 26.441 | 0.9496 | 24.12 | 0.375 | 9.525 |
| 1 | 11 | 0.0909 | 2.309 | 1.309 | 33.249 | 1.1926 | 30.292 | 0.4091 | 10.391 |
| 1 ¼ | 11 | 0.0909 | 2.309 | 1.65 | 41.91 | 1.5336 | 38.953 | 0.5 | 12.7 |
| 1 ½ | 11 | 0.0909 | 2.309 | 1.882 | 47.803 | 1.7656 | 44.846 | 0.5 | 12.7 |
| 2 | 11 | 0.0909 | 2.309 | 2.347 | 59.614 | 2.2306 | 56.657 | 0.625 | 15.875 |
| 2 ½ | 11 | 0.0909 | 2.309 | 2.96 | 75.184 | 2.8436 | 72.227 | 0.6875 | 17.463 |
| 3 | 11 | 0.0909 | 2.309 | 3.46 | 87.884 | 3.3436 | 84.927 | 0.8125 | 20.638 |
| 4 | 11 | 0.0909 | 2.309 | 4.45 | 113.03 | 4.3336 | 110.073 | ||
NPT stands for National Pipe Thread and is an American standard thread. It may also be reffered to as MPT , MNPT or NPT (M) for male external threads and FPT, FNPT or NPT(F) for female interal threads. A thread sealant must always be used to achieve a leak free seal (except for NPTF). It is also based on Trade Size rather than actual diameter (similar to BSP in this regard).
Both threads have the same pitch, angle (60 degrees) and shape (flat peaks and valleys).
The below table gives the Threads Per Inch, Pithc and Major Diameter for NPT Threads.
| Trade Size | Threads per inch | Pitch | Major Diameter (O.D) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inch | mm | Inch | mm | ||
| 1/8 | 27 | 0.03704 | 0.94082 | 0.405 | 10.29 |
| 1/4 | 18 | 0.05556 | 1.41122 | 0.54 | 13.72 |
| 3/8 | 18 | 0.05556 | 1.41122 | 0.675 | 17.15 |
| 1/2 | 14 | 0.07143 | 1.81432 | 0.84 | 21.34 |
| 3/4 | 14 | 0.07143 | 1.81432 | 1.05 | 26.67 |
| 1 | 11 ½ | 0.08696 | 2.20878 | 1.315 | 33.4 |
| 1 ¼ | 11 ½ | 0.08696 | 2.20878 | 1.66 | 42.16 |
| 1 ½ | 11 ½ | 0.08696 | 2.20878 | 1.9 | 48.26 |
| 2 | 11 ½ | 0.08696 | 2.20878 | 2.375 | 60.33 |
| 2 ½ | 8 | 0.125 | 3.175 | 2.875 | 73.03 |
| 3 | 8 | 0.125 | 3.175 | 3.5 | 88.9 |
| 4 | 8 | 0.125 | 3.175 | 4.5 | 114.3 |
BSP and NPT threads have more to do with where than what, which is an important distinction. Where NPT is prevalent in the U.S. and Canada, BSP is the primary standard in the UK, Europe, Asia, Australia, New Zealand, South Africa and many other countries.
NPT and BSP threads are not interchangeable due to the differences in thread forms. NPT threads are pointed in the peaks and valleys, where BSPs are rounded. Most notably, the NPT thread angle is 60 degrees versus the BSP 55-degree angle.
Though it has been tried, problems always arise when trying to thread a NPT male form into a BSPP female form. The dissimilar pitch will allow a misalignment of the threads, which causes leakage of fluid and even catastrophic failure under pressure.
| Trade Size | Pitch (Threads per Inch) | |
|---|---|---|
| NPT/NPS | BSP | |
| 1/8 | 27 | 28 |
| 1/4 | 18 | 19 |
| 3/8 | 18 | 19 |
| 1/2 | 14 | 14 |
| ¾ | 14 | 14 |
| 1 | 11 ½ | 11 |
| 1 ¼ | 11 ½ | 11 |
| 1 ½ | 11 ½ | 11 |
| 2 | 11 ½ | 11 |
| 2 ½ | 8 | 11 |
| 3 | 8 | 11 |
| 3 ½ | 8 | 11 |
| 4 | 8 | 11 |
| 5 | 8 | 11 |
| 6 | 8 | 11 |
To identify the trade size of the thread, first it must be determined whether the thread is tapered or parallel. This is done by measuring the first, fourth/fifth and last full thread. If the diameter increases from first thread to the last thread on a male thread or decreases from first to last thread on a female thread, then the thread is classified as a tapered thread (such as BSPT). If the diameter stays the same from the first to last thread then the thread is classified as a parallel thread (BSPP).
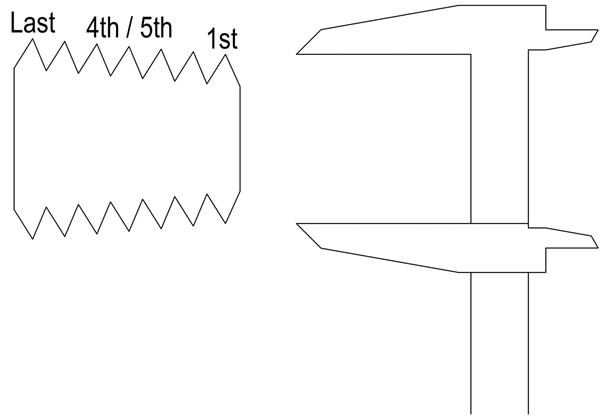
Once it is known whether the thread is parallel or tapered, it can be measured to determine it’s trade size. This trade size will not directly represent what is measured, ie. ½" BSP does not equal ½” measured. For a parallel thread, any thread can be used to measure for its trade size, and for a tapered thread the fourth or fifth full thread is used. This measurement can then be referenced against a thread table to match it to its trade size.
You may be interested in our range of Longwei Air Fittings including adaptors, quick coupler connectors, tire gauges, air blow gun, air chuck and tire repair tools kit, etc. If you have any further questions about the type of thread fitting you require, please contact the Longwei team today!